
Imagine wearing a winter parka in the tropics. This, in turn, over-insulates the planet. Modern climate change is caused by an excess of greenhouse gases.

If the Greenhouse Effect is Natural, Then What’s the Problem with Greenhouse Gases? Of the twenty greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide accounts for by far the largest share of radiative forcing since 1990, and its contribution continues to grow at a steady rate. Learn more about “climate forcing” greenhouse gases.Additional greenhouse gases include hydrofluorocarbons (1,430-14,800 time the global warming potential of carbon dioxide), sulfur hexafluoride (22,800 times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide), and water vapor.A single nitrous oxide molecule has 298 times the global warming potential of a carbon dioxide molecule. Modern agricultural practices - tilling and soil cultivation, livestock waste management, and the use of nitrogen-rich fertilizers - contribute significantly to nitrous oxide emissions. Nitrous oxide is released from bacteria in soil.Although methane emissions are lower than carbon dioxide emissions, it is considered a major greenhouse gas because each methane molecule has 25 times the global warming potential of a carbon dioxide molecule. Methane is caused by the decomposition of plant matter, and is released from landfills, swamps, rice paddies.In order to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, we need to reduce the amount of fuel we use in our cars, homes, and lives. Although carbon dioxide is not the most powerful greenhouse gas, it is the largest contributor to climate change because it is so common. Carbon dioxide, which is emitted whenever coal, oil, natural gas and other carbon-rich fossil fuels are burned.Some of the most common - and worrisome - greenhouse gases are: These gases form the insulation that keeps the planet warm enough to support life. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and other gases that accumulate in the atmosphere and create the heat-reflective layer that keeps the Earth at a livable temperature. Greater concentrations of greenhouse gases mean more solar radiation is trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere, making temperatures rise. Source: W.
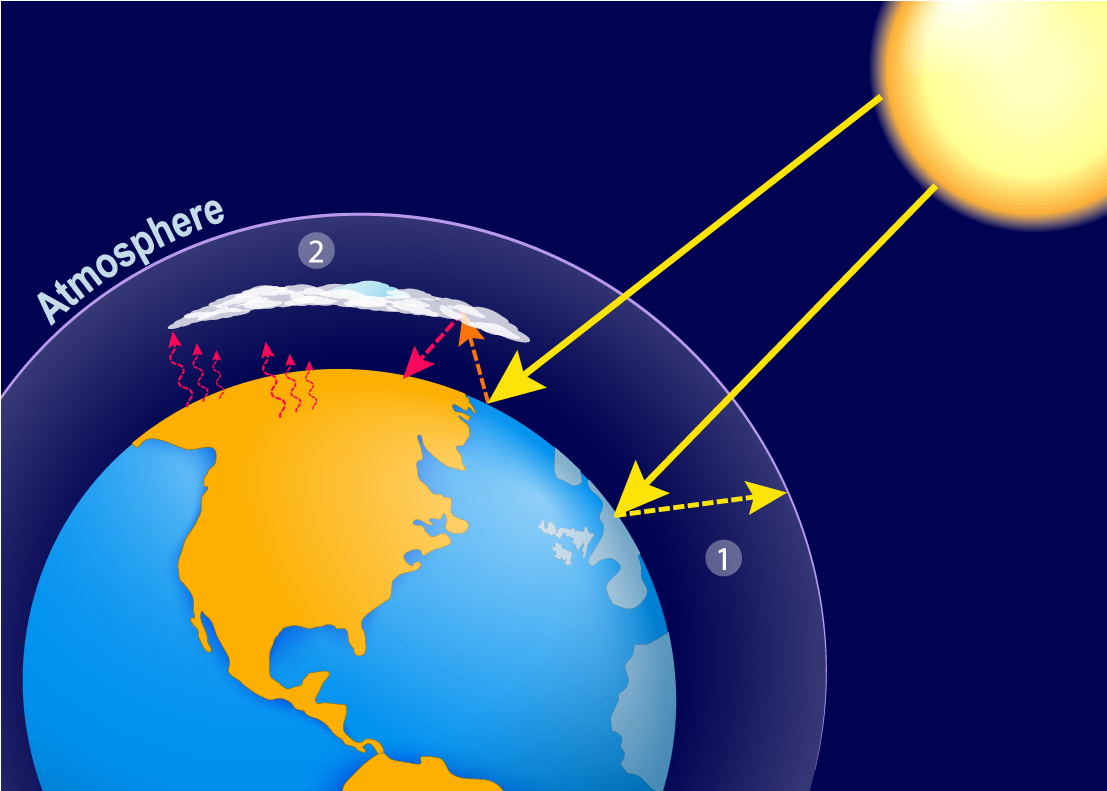
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb that heat, bouncing some back to the Earth’s surface and releasing some into the atmosphere. The Earth radiates heat back toward space. Clouds, ice caps and other light-colored surfaces reflect some light back into space, but most of the incoming energy reaches the planet’s surface. How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?Īlthough the process is complex, the greenhouse effect can be described fairly simply:


Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would not support most forms of life. The greenhouse effect is a natural process where atmospheric gases trap heat – a phenomena that allows the Earth to retain enough solar heat to be livable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
